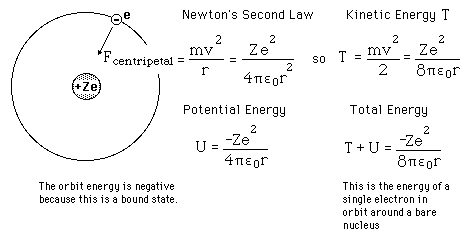
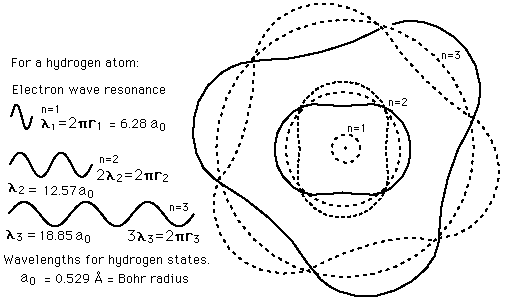
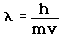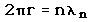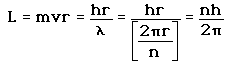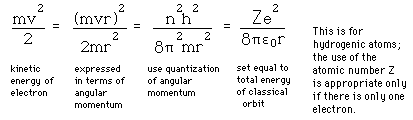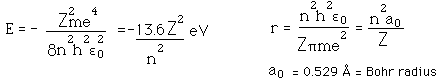Failures of the Bohr Model
While the Bohr model was a major step toward understanding the quantum theory of the atom, it is not in fact a correct description of the nature of electron orbits. Some of the shortcomings of the model are:
1. It fails to provide any understanding of why certain spectral lines are brighter than others. There is no mechanism for the calculation of transition probabilities.
2. The Bohr model treats the electron as if it were a miniature planet, with definite radius and momentum. This is in direct violation of the uncertainty principle which dictates that position and momentum cannot be simultaneously determined.
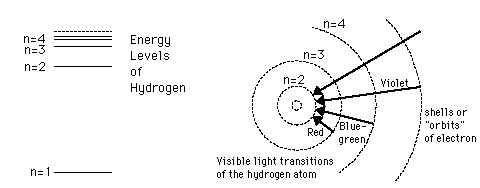
The Bohr model gives us a basic conceptual model of electrons orbits and energies. The precise details of spectra and charge distribution must be left to quantum mechanical calculations, as with the Schrodinger equation.
|